Changing a background color in Photoshop is one of the most essential and widely used photo editing skills in modern digital workflows. From eCommerce product images and professional portraits to furniture photography and marketing visuals, background color editing plays a crucial role in how an image is perceived, trusted, and converted.
At its core, changing a background color in Photoshop means separating the subject from its original background and placing it onto a new color while maintaining realism. This involves more than just selecting and filling a color—it requires accurate selection, clean edges, natural blending, and proper color harmony.
When done correctly, the final image looks natural and professionally shot. When done poorly, it immediately looks fake.
Quick Answer (Featured Snippet–Ready)
To change a background color in Photoshop, select the subject using tools like Quick Selection or the Pen Tool, apply a layer mask, add a solid color fill layer beneath the subject, and refine edges and colors to achieve a natural look.
This non-destructive approach ensures flexibility, accuracy, and professional results.
What Does “Changing Background Color” Really Mean?
Many beginners think background color change is simply “removing the background and adding a new color.” In reality, professionals treat it as a visual reconstruction process.
A proper background color change includes:
-
Accurate subject isolation
-
Smooth edge transitions
-
Matching brightness and contrast
-
Preserving natural shadows
-
Maintaining correct color temperature
Without these steps, even a technically correct selection will look unrealistic.
Why Background Color Matters So Much
Background color directly influences how viewers interpret an image—often subconsciously.
Key Reasons Background Color Is Critical
-
It controls visual focus
-
It affects brand consistency
-
It impacts trust and professionalism
-
It determines marketplace approval
-
It influences click-through and conversion rates
For example:
-
White or light gray backgrounds are trusted for eCommerce
-
Neutral tones work best for corporate portraits
-
Soft colors enhance furniture textures
-
Bold colors attract attention in ads
This is why professional image editing workflows always treat background color as a strategic decision, not a cosmetic one.
Who Needs to Change Background Color in Photoshop?
This skill is essential for:
-
eCommerce sellers (Amazon, Shopify, Etsy)
-
Photographers (product, portrait, real estate)
-
Designers & marketers
-
Fashion and apparel businesses
-
Advertising agencies
In many industries, poor background quality alone is enough to reduce sales—even if the product itself is excellent.
Photoshop vs Other Tools (Why Photoshop Still Leads)
While AI tools and online background changers exist, Photoshop remains the industry standard because it offers:
-
Full control over edges and masking
-
Non-destructive editing with layer masks
-
Advanced color correction tools
-
Manual shadow and reflection creation
-
High-resolution, print-ready output
AI tools are fast, but they struggle with:
-
Hair and fur
-
Transparent objects
-
Fine edges
-
Realistic shadows
For professional and commercial work, Photoshop delivers unmatched accuracy.
What Makes a Background Color Change Look Professional?
A professional background color change has these characteristics:
-
No jagged or harsh edges
-
No white or dark halos around the subject
-
Natural shadows and grounding
-
Correct color balance between subject and background
-
No loss of texture or detail
If any of these elements are missing, the edit looks artificial.
Common Beginner Misconception
One of the biggest mistakes beginners make is focusing only on selection tools.
In reality:
-
Selection is only 40% of the work
-
Mask refinement is 30%
-
Color, shadow, and blending are the remaining 30%
Professional results come from combining all three stages carefully.
What You Will Learn in This Complete Guide
This guide is structured to take you from beginner to professional level. In the upcoming parts, you’ll learn:
-
Multiple ways to change background color in Photoshop
-
Which method works best for different image types
-
Advanced techniques professionals use
-
How to avoid common mistakes
-
How to achieve realistic, commercial-ready results
Each part builds on the previous one, so even beginners can follow along confidently.
When and Why You Should Change Background Color in Photoshop (Strategy & Use Cases)
Changing a background color in Photoshop is not only about making an image look clean—it’s about communicating the right message to the viewer. The background color you choose can influence perception, trust, and even buying decisions.
Professionals don’t change background colors randomly. They do it strategically, based on purpose, platform, and audience.
When Should You Change a Background Color?
Not every image needs a background color change. Knowing when to apply it is just as important as knowing how.
You should change background color when:
-
The original background is distracting
-
The background color clashes with the subject
-
The image doesn’t meet marketplace requirements
-
You need visual consistency across multiple images
-
You want to align visuals with brand identity
A well-chosen background simplifies the image and improves clarity.
Why Background Color Has a Psychological Impact
Background color affects viewers on a subconscious level. Different colors trigger different emotions, which is why color choice is critical in commercial images.
Common Background Color Effects:
-
White: Clean, professional, trustworthy
-
Gray: Neutral, modern, balanced
-
Blue: Calm, reliable, corporate
-
Beige: Warm, natural, lifestyle-oriented
-
Bold colors: Attention-grabbing, promotional
For example:
-
eCommerce platforms favor white backgrounds
-
Corporate headshots look best on neutral tones
-
Ads perform better with high-contrast backgrounds
Professional editors consider these psychological effects before selecting a background color.
Why Businesses Rely on Background Color Editing
Background color consistency builds brand trust. When customers see uniform images across a website or catalog, they perceive the brand as more professional and reliable.
Business Benefits:
-
Higher product clarity
-
Improved brand recognition
-
Increased conversion rates
-
Stronger visual storytelling
This is why background color editing is a standard part of professional image editing services.
Platform-Specific Background Color Requirements
Different platforms have different expectations—and sometimes strict rules.
eCommerce Marketplaces:
-
Amazon prefers white backgrounds
-
Shopify allows flexibility but favors consistency
-
Etsy encourages clean, neutral backgrounds
Corporate & Professional Use:
-
Neutral or muted colors
-
Minimal distractions
-
Consistent across teams or departments
Advertising & Social Media:
-
Creative colors allowed
-
Strong contrast improves engagement
-
Brand colors perform better
Understanding platform expectations prevents image rejection and improves performance.
When Not to Change the Background Color
There are cases where changing the background color can actually harm the image.
Avoid background color change when:
-
The original background supports the story
-
Environmental context is important
-
Natural lighting cannot be replicated
-
The subject blends poorly with flat colors
In lifestyle photography, keeping the original background often preserves authenticity.
How Professionals Decide the Right Background Color
Professionals follow a simple decision process:
-
Identify the image purpose
-
Consider platform guidelines
-
Analyze subject color and texture
-
Choose a background that enhances contrast
-
Test for realism and balance
The goal is never to overpower the subject, but to support it visually.
Background Color Change vs Background Removal
Many people confuse these two concepts.
-
Background removal focuses on isolating the subject
-
Background color change focuses on visual harmony
Removal is just one step. Color change completes the image.
Professional results require both.
Real-World Example Scenarios
-
A product photo with a cluttered background loses buyer trust
-
A portrait with a bright background distracts from the face
-
Furniture images without neutral backgrounds look unrealistic
-
Ads with low contrast fail to attract attention
In all these cases, background color change improves clarity and impact.
What You Need Before Changing Background Color in Photoshop (Tools, Setup & Preparation)

Before you change a background color in Photoshop, preparation is critical. Most poor-quality background edits don’t fail because of bad tools—they fail because of poor setup and rushed preparation.
Professional editors spend time preparing the image before making any selections. This step alone can dramatically improve edge quality, realism, and overall results.
Why Preparation Matters More Than Tools
Many beginners jump straight into selecting the subject. Professionals don’t.
Proper preparation helps you:
-
Create cleaner selections
-
Reduce jagged edges and halos
-
Preserve fine details (hair, texture, fabric)
-
Save time during masking and refinement
In short, preparation determines whether your final image looks amateur or professional.
Essential Requirements Before You Start
1️⃣ Adobe Photoshop (Version Matters Less Than Skill)
Any modern version of Photoshop works well for background color changes. Tools like:
-
Select Subject
-
Select and Mask
-
Layer Masks
are available in most recent versions.
What matters more is understanding how and when to use them.
2️⃣ High-Quality Image (Very Important)
Image quality directly affects selection accuracy.
Best Practices:
-
Use high-resolution images whenever possible
-
Avoid heavily compressed or blurry photos
-
Clear lighting helps define edges
⚠️ Important:
No Photoshop technique can fully fix poor image quality. Clean input = clean output.
3️⃣ Clean and Organized Photoshop Workspace
Before editing:
-
Open the Layers panel
-
Ensure the Properties panel is visible
-
Keep History panel accessible
Professional editors always work in an organized workspace to avoid mistakes.
Photoshop Tools You Must Understand Before Changing Background Color
🔹 Selection Tools (Core Tools)
You don’t need to master every tool—only the right ones.
Most Important Selection Tools:
-
Quick Selection Tool – Fast, beginner-friendly
-
Select Subject – AI-powered, time-saving
-
Pen Tool – Maximum accuracy for products and furniture
Each tool serves a different purpose. Choosing the right one saves hours.
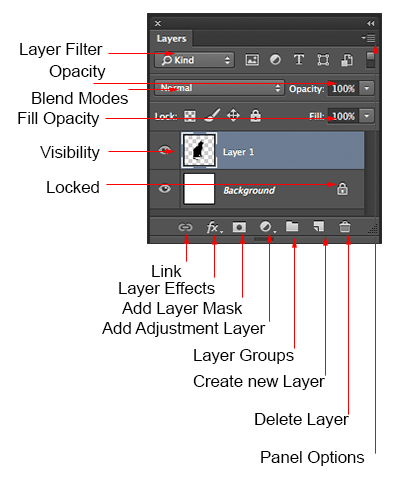
🔹 Layer Masks (Non-Destructive Editing)
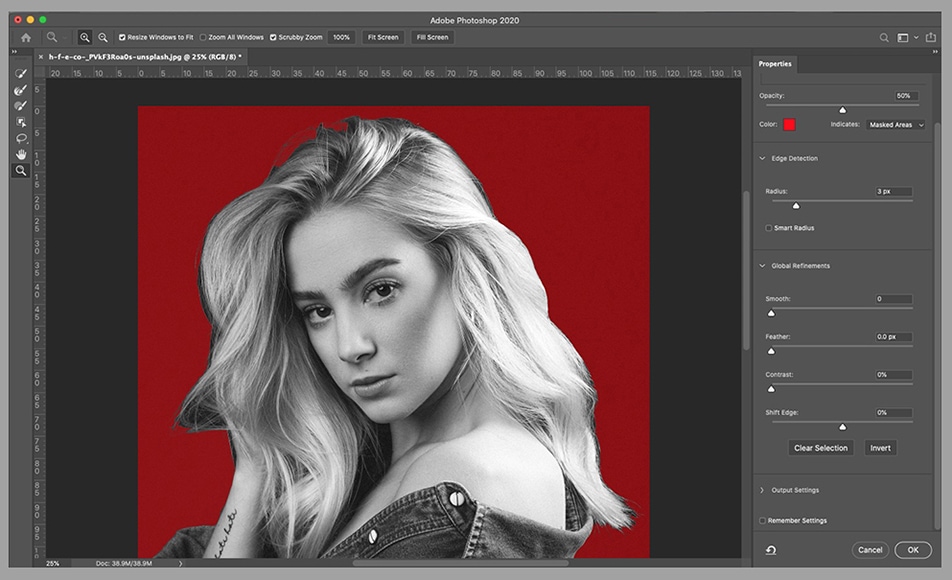
Layer masks are essential for professional background color changes.
They allow you to:
-
Hide or reveal areas without deleting pixels
-
Fix mistakes anytime
-
Refine edges gradually
Professional rule:
Never erase backgrounds. Always use layer masks.
🔹 Adjustment & Fill Layers

For background color change, you’ll mainly use:
-
Solid Color Fill Layers
-
Curves
-
Hue/Saturation
-
Color Balance
These help you match brightness, contrast, and color harmony between subject and background.
Preparing the Image Before Selection (Critical Step)
Before selecting the subject:
-
Zoom in to 200–300%
-
Check edge clarity
-
Remove obvious dust or spots
-
Fix extreme exposure issues
This makes the selection process smoother and more accurate.
Duplicate Layers for Safety
Professional workflow always includes backups.
Best Practice:
-
Duplicate the original image layer
-
Lock the original layer
-
Work only on duplicates
This ensures you can always revert if something goes wrong.
Understanding Edge Complexity Before You Start
Not all edges are equal.
Easy Edges:
-
Hard objects
-
Clean product outlines
Difficult Edges:
-
Hair and fur
-
Fabric fibers
-
Transparent materials
Knowing this helps you decide:
-
Which tool to use
-
How much time to spend
-
Whether advanced masking is required
Common Preparation Mistakes to Avoid
❌ Starting selection at 100% zoom
❌ Using eraser instead of masks
❌ Ignoring image quality issues
❌ Rushing into color fill without checking edges
Most problems later come from skipping preparation.
Method 1 – How to Change Background Color Using the Quick Selection Tool (Beginner-Friendly Method)

The Quick Selection Tool is the easiest and fastest way to change a background color in Photoshop. It is ideal for beginners and works best when the subject is clearly separated from the background.
This method relies on Photoshop’s smart edge detection, allowing you to select the subject by simply brushing over it.
When to Use the Quick Selection Tool
This method is best for:
-
Simple backgrounds
-
High-contrast subjects
-
Products with clear edges
-
People without complex hair
⚠️ Avoid this method for:
-
Hairy or fuzzy edges
-
Transparent objects
-
Detailed fabric textures
Step-by-Step: Change Background Color with Quick Selection Tool
Step 1: Open and Prepare the Image
-
Open your image in Photoshop
-
Duplicate the background layer
-
Lock the original layer for safety
This ensures a non-destructive workflow.
Step 2: Select the Quick Selection Tool
-
Choose the Quick Selection Tool (W)
-
Set a medium brush size
-
Make sure “Sample All Layers” is unchecked
Brush size control is critical for clean selections.
Step 3: Select the Subject
-
Click and drag over the subject
-
Photoshop automatically expands the selection
-
Hold Alt/Option to remove unwanted areas
Zoom in while selecting to avoid edge mistakes.
Step 4: Refine the Selection (Very Important)
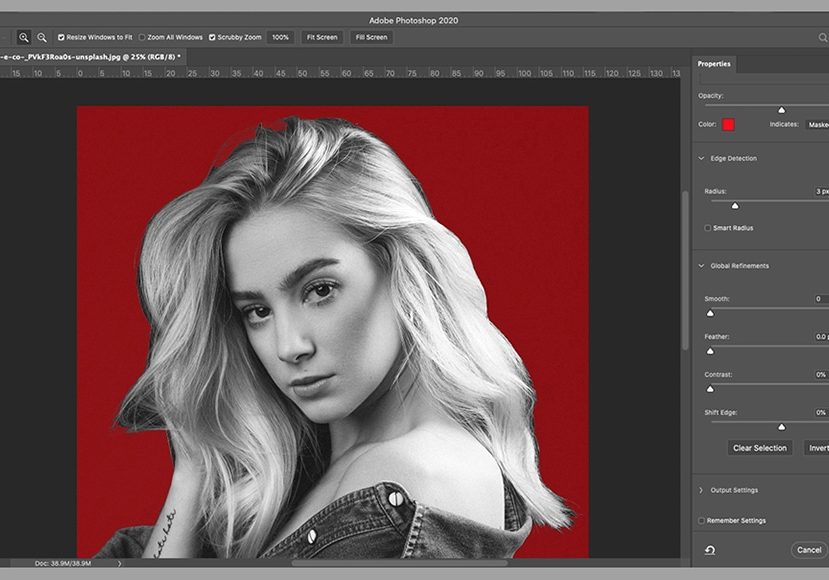
-
Click Select and Mask
-
Adjust:
-
Smooth (reduce jagged edges)
-
Feather (slight softness)
-
Contrast (sharper edge)
-
-
Use Refine Edge Brush around hair or soft areas
This step separates amateur results from professional ones.
Step 5: Apply a Layer Mask
-
Click Add Layer Mask
-
The background becomes hidden
-
The subject remains intact
Never delete the background—always mask it.
Step 6: Add a New Background Color
-
Go to Layer > New Fill Layer > Solid Color
-
Choose your desired background color
-
Place the color layer below the subject layer
This instantly changes the background color.
Step 7: Fine-Tune the Edges
-
Select the layer mask
-
Use a soft black or white brush
-
Paint gently to clean edges
Work at low opacity (10–30%) for natural results.
How to Choose the Right Background Color
When choosing a background color:
-
Ensure strong contrast with the subject
-
Avoid oversaturated colors
-
Use off-white instead of pure white
-
Match the mood of the image
Professional edits prioritize realism over brightness.
Common Problems & Quick Fixes
❌ Jagged edges
✔ Use Select and Mask → Smooth
❌ Halo around subject
✔ Paint mask edges with soft brush
❌ Subject looks flat
✔ Add a soft shadow under the subject
Limitations of This Method
While fast and easy, the Quick Selection Tool has limitations:
-
Struggles with complex edges
-
Inaccurate for transparent objects
-
Often leaves halos
For professional or commercial images, advanced methods are preferred.
Method 2 – How to Change Background Color Using Layer Masks (Professional & Non-Destructive Method)

If you want clean, realistic, and professional results, changing background color using Layer Masks is the correct approach. Unlike quick methods, this technique gives you full control and allows unlimited corrections without damaging the original image.
This is the method used in professional photo retouching, product editing, portrait editing, and commercial workflows.
Why Layer Masks Are the Professional Standard
Layer masks allow you to hide or reveal parts of a layer without deleting pixels. This makes your edit:
-
Fully reversible
-
More precise
-
Safer for high-resolution images
-
Suitable for client or commercial work
Professional rule:
If you erase pixels, you’re doing destructive editing. Professionals never do that.
When You Should Use the Layer Mask Method
This method is ideal for:
-
Portraits and headshots
-
Product photos
-
Furniture images
-
Fashion and apparel
-
Any image that needs high accuracy
It works especially well when the subject has soft edges or when you need to refine details over time.
Step-by-Step: Change Background Color Using Layer Masks
Step 1: Open and Prepare the Image
-
Open the image in Photoshop
-
Duplicate the background layer
-
Lock the original layer
This protects your original file and keeps your workflow clean.
Step 2: Select the Subject
You can use:
-
Select Subject (fast and accurate for many images)
-
Quick Selection Tool (manual control)
-
Pen Tool (highest accuracy for products and furniture)
The better the selection, the better the final result.
Step 3: Add a Layer Mask
-
With the subject selected, click Add Layer Mask
-
The background becomes hidden
-
The subject remains visible
At this stage, don’t worry about perfection. Refinement comes next.
Step 4: Create a New Background Color Layer
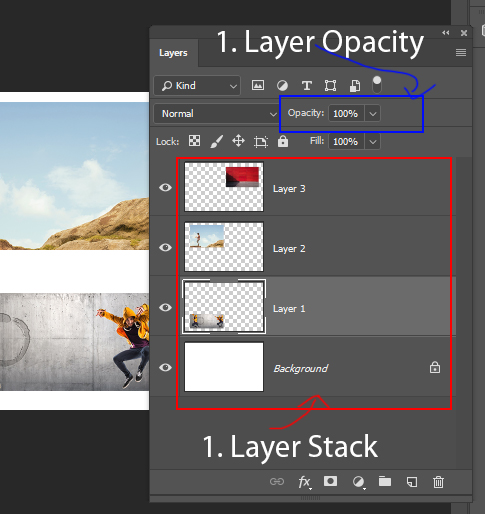
-
Go to Layer > New Fill Layer > Solid Color
-
Choose your desired background color
-
Place this layer below the subject layer
You now have a clean background color behind your subject.
Refining Edges for a Natural Look (Critical Step)
This is where professional results are created.
How to Refine:
-
Click on the Layer Mask
-
Select a soft round brush
-
Use black to hide unwanted areas
-
Use white to restore details
-
Work at 10–30% opacity
Zoom in to 200–300% and work slowly.
Handling Hair, Fabric & Soft Edges
For hair and soft edges:
-
Use Select and Mask
-
Refine with Refine Edge Brush
-
Slight feathering helps realism
-
Avoid hard brush strokes
Pro Tip:
Perfect edges look fake. Slight softness looks natural.
Matching the Subject with the New Background
Once the background color is changed, adjust the subject to match it.
Important Adjustments:
-
Curves → Match brightness
-
Color Balance → Match temperature
-
Hue/Saturation → Reduce color mismatch
These small adjustments prevent the “cut-and-paste” look.
Adding Depth with Shadows
A background color alone can make the subject look flat.
To fix this:
-
Create a new layer under the subject
-
Paint a soft shadow with a black brush
-
Reduce opacity (10–20%)
-
Blur slightly
This grounding shadow adds realism instantly.
Common Mistakes with Layer Masks
❌ Using a hard brush on edges
❌ Over-feathering the mask
❌ Ignoring color temperature
❌ Forgetting shadows
Layer masks give control—but only if used patiently.
Advantages of the Layer Mask Method
✔ Non-destructive
✔ Professional quality
✔ Unlimited refinement
✔ Works for complex images
✔ Industry-standard technique
This is the method professionals rely on for commercial-ready images.
Method 3 – How to Change Background Color Using the Pen Tool (Most Accurate Method)
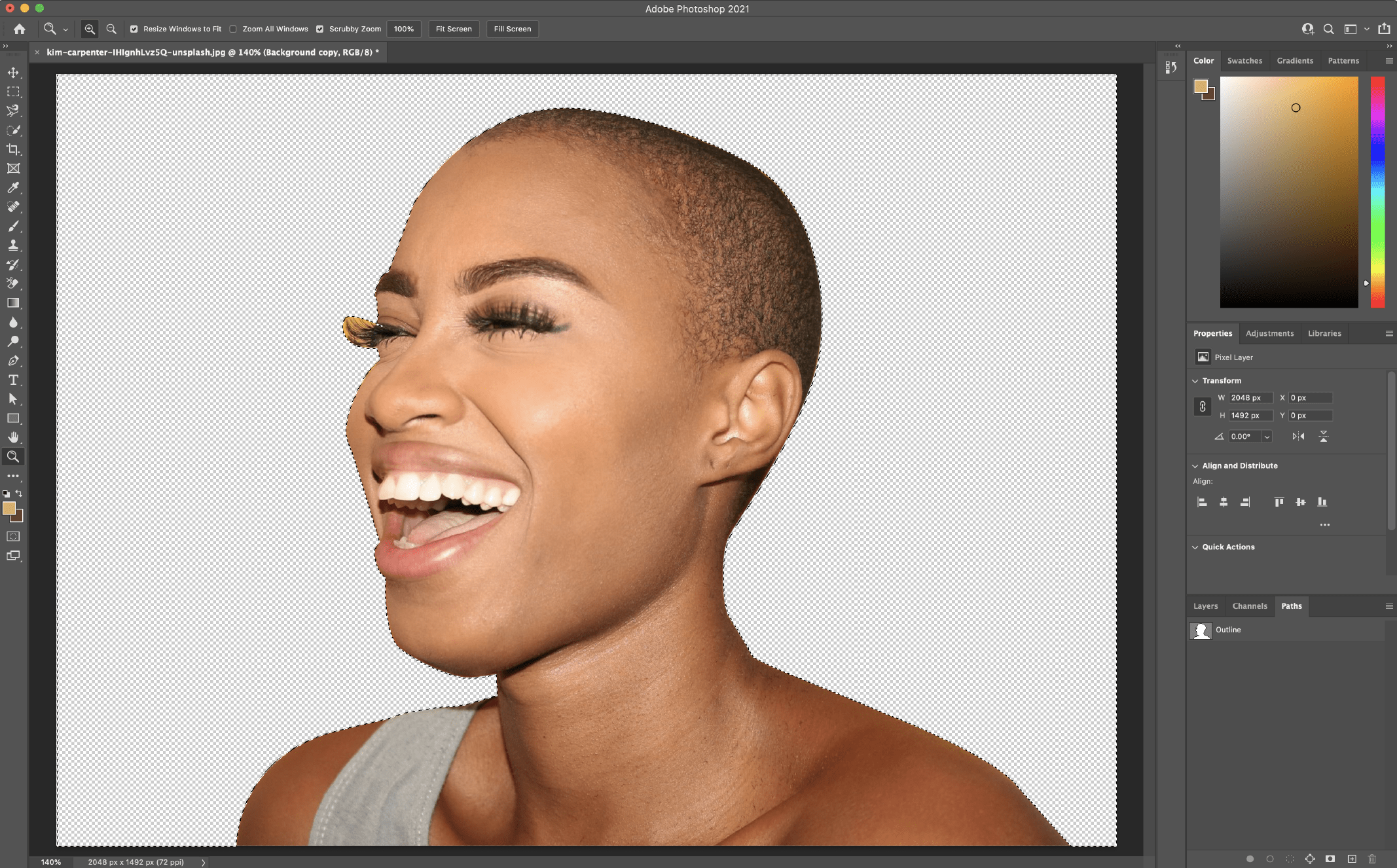
When precision matters, the Pen Tool is the most accurate way to change a background color in Photoshop. Unlike automated selection tools, the Pen Tool gives you complete manual control over every curve and edge.
This is the preferred method for:
-
Product photos
-
Furniture images
-
Electronics
-
Hard-edged objects
-
Commercial and print-ready work
If you want pixel-perfect edges, this is the method to master.
Why the Pen Tool Produces the Cleanest Results
The Pen Tool creates vector-based paths, not pixel-based selections. This means:
-
Smooth, sharp edges
-
No jagged pixels
-
Consistent results at any zoom level
-
Ideal for high-resolution images
While it takes more time, the quality difference is significant—especially for professional use.
When You Should Use the Pen Tool
Use the Pen Tool when:
-
The subject has hard, defined edges
-
The image is for eCommerce or advertising
-
Accuracy is more important than speed
-
AI or Quick Selection fails
⚠️ Avoid using it for:
-
Hair and fur
-
Soft, transparent edges
Those require masking or channel techniques.
Step-by-Step: Change Background Color Using the Pen Tool
Step 1: Select the Pen Tool
-
Choose the Pen Tool (P)
-
Set mode to Path
-
Zoom in to at least 200%
Working slowly is essential for accuracy.
Step 2: Create a Path Around the Subject
-
Click to create anchor points
-
Drag to create smooth curves
-
Follow the natural shape of the subject
-
Use fewer points for smoother paths
Professional Tip:
More anchor points do not mean better accuracy. Fewer, well-placed points produce cleaner edges.
Step 3: Close the Path
-
Complete the path by clicking the first anchor point
-
Ensure the path fully encloses the subject
Check carefully for gaps before moving on.
Step 4: Convert Path to Selection
-
Open the Paths panel
-
Right-click → Make Selection
-
Set feather radius to 0.5–1 px (for realism)
This creates a clean, accurate selection.
Step 5: Apply a Layer Mask
-
With the selection active, click Add Layer Mask
-
The background is now hidden
-
The subject remains visible
You now have a perfectly cut subject.
Step 6: Add a New Background Color
-
Create a Solid Color Fill Layer
-
Choose your desired background color
-
Place it below the subject layer
The background color is instantly replaced.
Refining Pen Tool Edges (Pro-Level Touch)
Even with perfect paths, minor refinement improves realism.
Refinement Tips:
-
Slight feathering prevents harsh edges
-
Zoom in and inspect curves
-
Manually clean corners with mask brush
Rule:
Perfectly sharp edges often look fake. Subtle softness looks natural.
Adding Natural Shadows for Realism
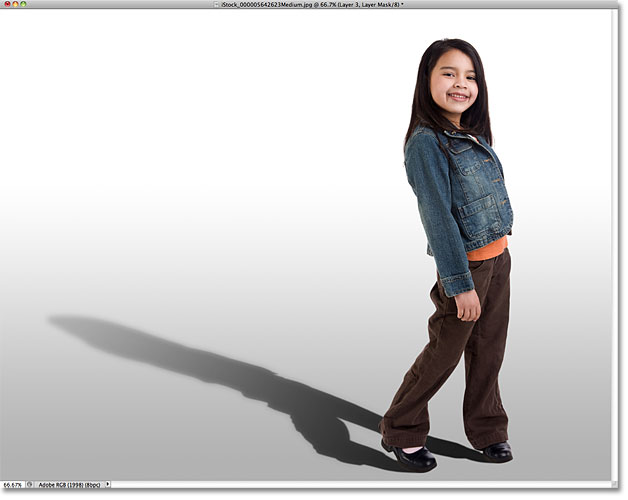

After background color change:
-
Create a new layer under the subject
-
Paint soft shadows using a low-opacity black brush
-
Blur slightly if needed
This anchors the subject to the background and prevents floating effects.
Common Pen Tool Mistakes to Avoid
❌ Using too many anchor points
❌ Sharp corners where curves are needed
❌ Forgetting feather settings
❌ Skipping shadow creation
Patience and practice make this method powerful.
Advantages of the Pen Tool Method
✔ Maximum edge accuracy
✔ Ideal for commercial use
✔ Scales well for bulk editing
✔ Preferred for eCommerce & furniture
The Pen Tool remains the industry standard for clipping path and background color replacement.
How to Make the New Background Color Look Natural (Color Matching, Shadows & Realism)
Changing a background color is only half the job. The real challenge is making the subject and background belong together. Without proper color matching, lighting adjustment, and shadows, the image will look cut out—even if the selection is perfect.
Professional editors spend more time on this stage than on selection itself.
Why Background Color Changes Often Look Fake
Most unnatural edits suffer from one or more of these problems:
-
Subject brightness doesn’t match the background
-
Color temperature is inconsistent
-
No grounding shadow
-
Background is too flat or too saturated
The human eye instantly notices these mismatches.
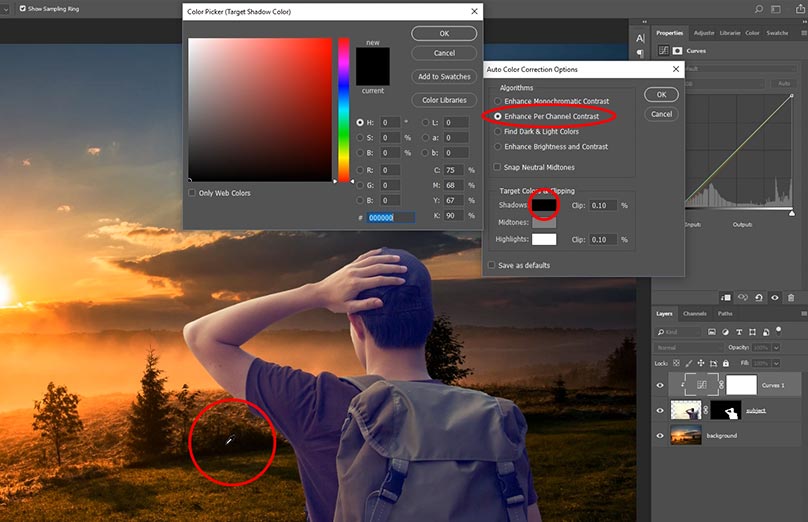
Step 1: Match Brightness and Contrast (Critical First Step)


Before adjusting color, match light levels.
How to Do It:
-
Add a Curves adjustment layer
-
Clip it to the subject layer
-
Adjust highlights and shadows to match the background
Professional Tip:
If the subject is brighter than the background, it will look pasted on. Always balance brightness first.
Step 2: Match Color Temperature (Warm vs Cool)
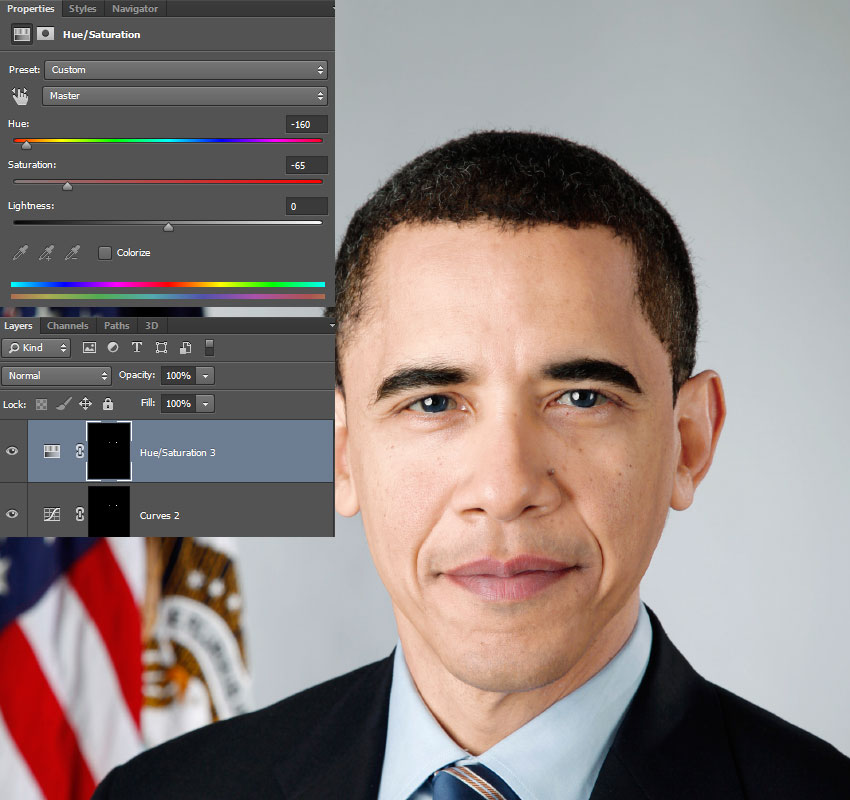
Every image has a color temperature:
-
Warm (yellow/orange tones)
-
Cool (blue tones)
How to Match:
-
Use Color Balance
-
Adjust midtones first
-
Match background warmth to subject or vice versa
Even a small mismatch makes the edit look artificial.
Step 3: Adjust Saturation for Realism
Over-saturated backgrounds are a common mistake.
Best Practice:
-
Reduce saturation slightly (5–15%)
-
Avoid pure RGB colors
-
Use muted tones for realism
Pro Tip:
Pure white (#FFFFFF) and pure black (#000000) rarely look natural. Slight off-white or dark gray works better.
Step 4: Add Natural Shadows (Most Missed Step)
Without shadows, subjects look like they’re floating.
How to Create a Soft Ground Shadow:
-
Create a new layer under the subject
-
Use a soft black brush at 10–20% opacity
-
Paint lightly under contact areas
-
Apply slight Gaussian Blur
Shadows should be subtle—not dramatic.
Step 5: Match Edge Softness
Edges that are too sharp often look fake.
Fix It By:
-
Slightly feathering the mask (0.5–1px)
-
Softening edges with a low-opacity brush
-
Avoiding hard transitions
Natural edges are rarely razor-sharp.
Step 6: Add Background Texture or Gradient (Optional but Powerful)
Flat backgrounds can look unnatural in some cases.
When to Use:
-
Portraits
-
Furniture images
-
Marketing visuals
How:
-
Add a subtle gradient
-
Introduce very light noise
-
Keep texture extremely soft
This adds depth without distraction.
Professional Checklist for Realism
Before finalizing, check:
-
Does the light direction match?
-
Are shadows present?
-
Is color temperature consistent?
-
Are edges natural?
-
Does anything feel “cut out”?
If something feels off, it usually is.
Common Mistakes That Kill Realism
❌ Ignoring shadows
❌ Over-saturated backgrounds
❌ Mismatched brightness
❌ Pure white backgrounds
❌ Over-feathered edges
Fixing these instantly improves quality.
Common Background Color Change Mistakes in Photoshop (And How to Fix Them Like a Pro)
Even when you follow the correct steps, background color changes can still look unnatural. That’s because most issues don’t come from the tools themselves—they come from small technical mistakes that compound visually.
In this part, we’ll break down the most common background color change mistakes in Photoshop and show you exactly how professionals fix them.
Mistake 1: Jagged or Rough Edges Around the Subject
Why It Happens
-
Low-resolution images
-
Poor selection refinement
-
Using hard brushes on masks
Jagged edges are one of the fastest ways to make an edit look amateur.
How to Fix It
-
Zoom in to 200–300%
-
Open Select and Mask
-
Increase Smooth slightly
-
Add 0.5–1 px feather
-
Use a soft brush on the layer mask
Pro Tip:
Edges should look natural—not perfectly sharp.
Mistake 2: White or Dark Halo Around the Subject
Why It Happens
-
Original background color bleeding into edges
-
Poor masking around hair or fine details
Halos are especially visible on dark or colored backgrounds.
How to Fix It
-
Open Select and Mask
-
Enable Decontaminate Colors
-
Use Defringe (1–2 px) if needed
-
Manually clean edges with low-opacity brush
This removes leftover background color contamination.
Mistake 3: Subject Looks Like It’s Floating
Why It Happens
-
No grounding shadow
-
Flat background color
-
Ignoring light direction
Without shadows, the subject has no connection to the background.
How to Fix It
-
Create a new layer under the subject
-
Paint a soft black shadow (10–20% opacity)
-
Blur slightly for realism
-
Match shadow direction to light source
Shadows should be subtle, not dramatic.
Mistake 4: Background Color Looks Too Strong or Fake
Why It Happens
-
Over-saturated colors
-
Using pure RGB colors
-
No tonal balance
Bright backgrounds easily overpower the subject.
How to Fix It
-
Reduce saturation by 5–15%
-
Use muted or off-white tones
-
Match background brightness with Curves
-
Avoid pure white (#FFFFFF)
Professional backgrounds are rarely pure colors.
Mistake 5: Mismatched Color Temperature


Why It Happens
-
Subject shot in warm light
-
Background color is cool (or vice versa)
Even subtle temperature differences look unnatural.
How to Fix It
-
Use Color Balance
-
Adjust midtones first
-
Match background warmth to subject
-
Fine-tune highlights and shadows
Consistency matters more than accuracy.
Mistake 6: Over-Feathered or Blurry Edges
Why It Happens
-
Too much feathering
-
Heavy blur on mask
-
Over-smoothing in Select and Mask
Over-feathering makes the subject look soft and unrealistic.
How to Fix It
-
Reduce feather to under 1 px
-
Increase mask contrast slightly
-
Manually sharpen edges where needed
Edges should be clean but natural.
Mistake 7: Using the Eraser Tool Instead of Masks
Why It Happens
-
Beginner habit
-
Lack of non-destructive workflow
Once erased, pixels are gone forever.
How to Fix It
-
Stop using the Eraser Tool
-
Always use Layer Masks
-
Paint with black/white instead
Non-destructive editing is mandatory for professional work.
Mistake 8: Ignoring Image Quality Limits

Why It Happens
-
Low-resolution or compressed images
-
Motion blur or noise
Photoshop can’t create detail that doesn’t exist.
How to Fix It
-
Work with highest-quality source files
-
Reduce expectations on low-res images
-
Avoid extreme background contrasts
Sometimes the limitation is the image—not your skill.
Professional Troubleshooting Checklist
Before final export, ask:
-
Are edges clean at 300% zoom?
-
Is there any halo or color bleed?
-
Do shadows match the light direction?
-
Does the background overpower the subject?
-
Does the image feel natural?
If the answer is “no” to any of these, refine further.
Photoshop vs AI & Online Background Color Tools (Which One Should You Use?)

With the rise of AI-powered tools, many people ask:
“Why use Photoshop when AI tools can change background color instantly?”
The answer depends on quality, control, and purpose. In this part, we’ll compare Photoshop vs AI and online background color tools honestly—so you know exactly which option fits your needs.
Overview: Photoshop vs AI Tools
At a glance, AI tools focus on speed, while Photoshop focuses on accuracy and realism.
| Feature | Photoshop | AI / Online Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Very high | Medium |
| Edge Control | Full manual | Limited |
| Hair & Details | Excellent (manual) | Often fails |
| Shadows & Realism | Fully customizable | Minimal or none |
| Commercial Use | Safe & professional | Risky |
| Speed | Slower | Very fast |
How AI Background Color Tools Work
AI tools use machine learning to:
-
Detect the subject automatically
-
Remove or replace the background
-
Apply preset colors or styles
Popular AI tools include:
-
Online background changers
-
Mobile apps
-
Built-in website editors
They are designed for quick results, not perfection.
Strengths of AI & Online Tools
AI tools are useful when:
-
You need instant results
-
Image quality requirements are low
-
Backgrounds are very simple
-
You’re creating casual content
Advantages:
✔ Extremely fast
✔ No Photoshop skills required
✔ Beginner-friendly
✔ Often free or low-cost
For social media or personal use, AI tools can be enough.
Limitations of AI Tools (Important)

AI tools struggle with:
-
Hair and fur
-
Transparent objects
-
Fine edges
-
Color contamination
-
Realistic shadows
They often:
-
Leave halos
-
Flatten depth
-
Ignore lighting direction
These flaws are immediately noticeable in professional or commercial images.
Why Photoshop Still Dominates Professional Work
Photoshop allows editors to:
-
Control every pixel manually
-
Choose the best selection method
-
Refine edges precisely
-
Match color, light, and texture
-
Create natural shadows and depth
For:
-
eCommerce product images
-
Furniture photos
-
Fashion & apparel
-
Advertising creatives
Photoshop remains the industry standard.
Speed vs Quality: The Real Trade-Off
AI tools win on speed. Photoshop wins on quality.
Choose AI tools if:
-
Speed matters more than quality
-
The image is low-stakes
-
You don’t need perfection
Choose Photoshop if:
-
Image quality affects sales
-
You need realistic results
-
The image is client-facing
-
Brand consistency matters
Professional brands always choose quality.
Commercial & Legal Considerations
This is often overlooked.
AI Tools:
-
May compress image quality
-
Sometimes restrict commercial usage
-
Limited export control
Photoshop:
-
Full ownership of edits
-
High-resolution exports
-
Safe for print and ads
For commercial projects, Photoshop is the safer choice.
Hybrid Workflow Used by Professionals
Some professionals use a hybrid approach:
-
Use AI for quick rough selection
-
Import into Photoshop
-
Refine edges manually
-
Add shadows and color matching
This saves time without sacrificing quality.
Which One Should You Choose? (Simple Answer)
-
Casual / personal use: AI tools
-
Professional / business use: Photoshop
-
High-volume + quality needs: Photoshop or professional services
There is no shortcut to realism.
Advanced Background Color Techniques in Photoshop (Gradients, Blend If, Reflections & Pro Tricks)
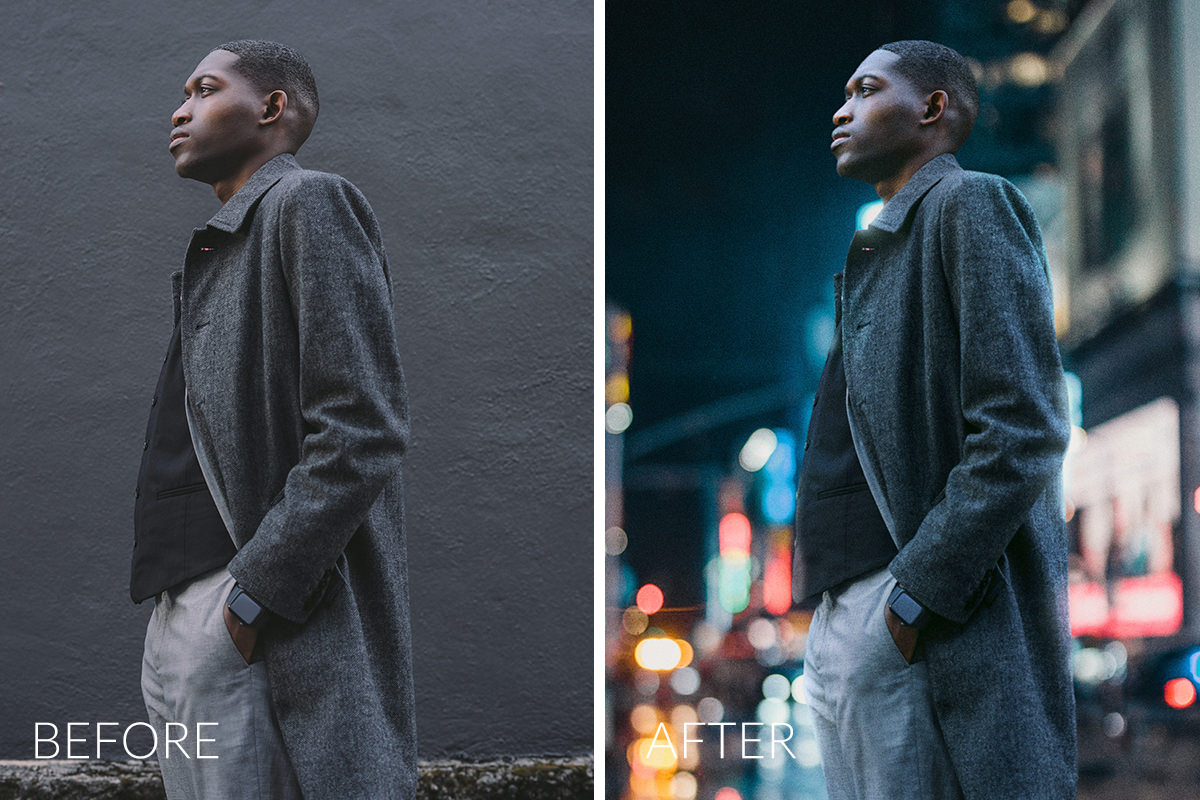

Once you understand the basics of changing background color in Photoshop, the next step is learning advanced techniques that add depth, realism, and polish. These methods are commonly used in advertising, eCommerce, furniture photography, and high-end retouching.
This part focuses on techniques professionals use to make background color changes look intentional and realistic, not flat or artificial.
Using Gradient Backgrounds Instead of Flat Colors
Flat background colors often look unnatural, especially for portraits, furniture, and lifestyle images. Gradients introduce subtle depth.
When to Use Gradients:
-
Portraits and headshots
-
Furniture and interior images
-
Marketing visuals
-
Editorial-style photos
How to Create a Gradient Background:
-
Add a Gradient Fill Layer
-
Choose a soft light-to-dark gradient
-
Keep contrast subtle
-
Position the lighter area near the subject
Professional Tip:
Gradients should be barely noticeable. If you can clearly see the gradient, it’s too strong.
Using “Blend If” for Natural Edge Blending
The Blend If sliders are one of Photoshop’s most powerful but underused tools.
What Blend If Does:
-
Blends layers based on brightness
-
Helps edges merge naturally
-
Reduces harsh transitions
How to Use Blend If:
-
Double-click the subject layer
-
Locate Blend If
-
Adjust the background sliders
-
Hold Alt/Option to split sliders for smooth blending
This technique is excellent for:
-
Hair edges
-
Soft shadows
-
Natural light blending
Adding Realistic Reflections (Products & Furniture)
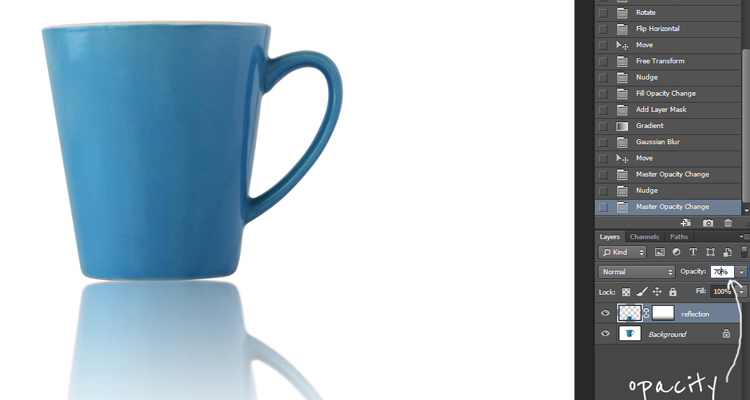

Reflections add realism, especially for:
-
Furniture
-
Electronics
-
Glass products
How to Create a Reflection:
-
Duplicate the subject layer
-
Flip it vertically
-
Lower opacity
-
Add a gradient mask
-
Blur slightly
Reflections should be subtle and never overpower the subject.
Matching Background Color with Subject Color (Color Harmony)
Advanced editors ensure the background complements—not competes with—the subject.
Best Practices:
-
Use muted background tones
-
Avoid matching subject color exactly
-
Create contrast through brightness, not saturation
Professional Insight:
A background that’s too similar in color reduces subject separation.
Using Noise and Texture for Realism
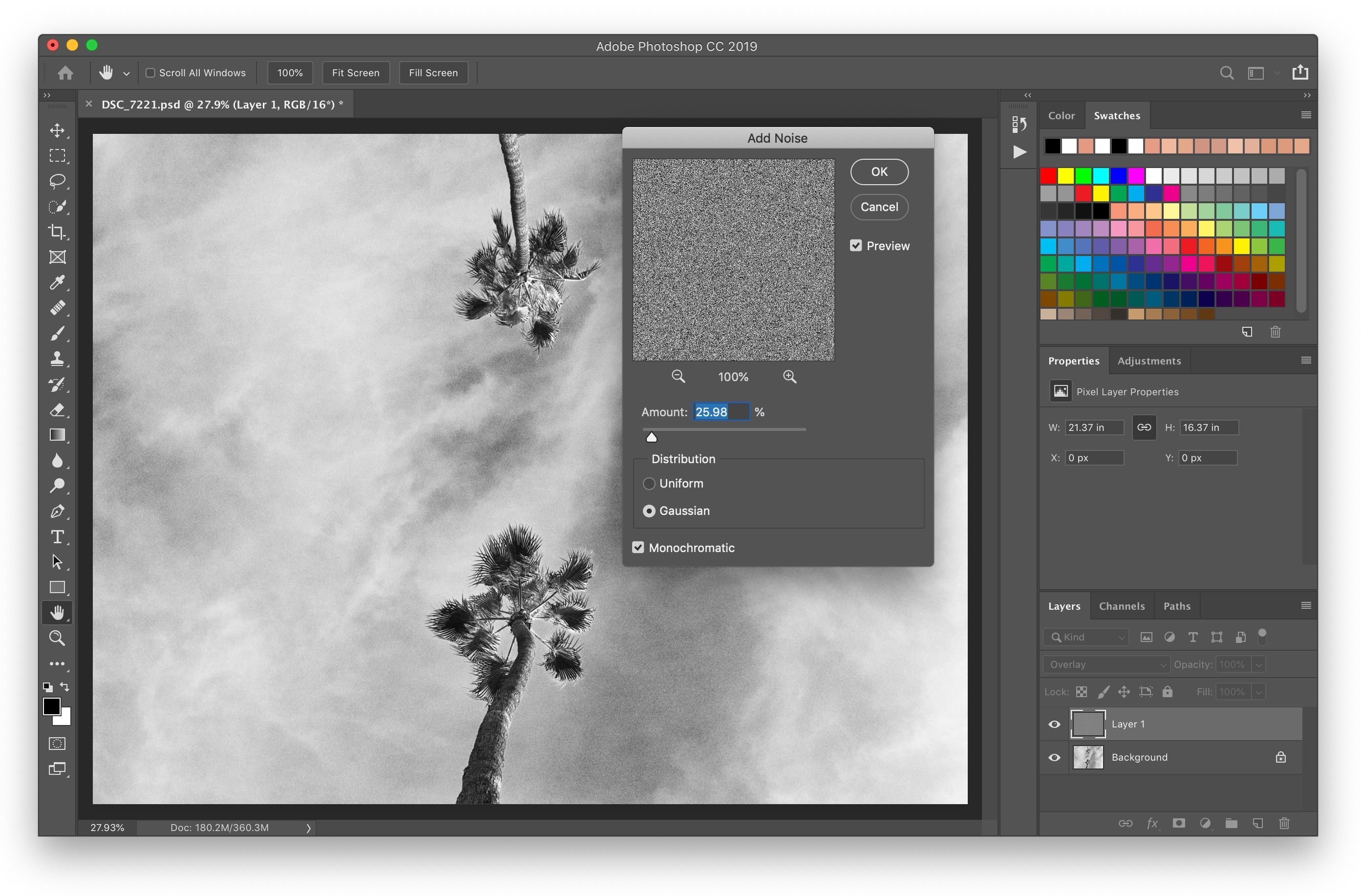
Perfectly smooth backgrounds often look fake.
How to Add Subtle Texture:
-
Add a new layer
-
Fill with 50% gray
-
Add minimal noise (1–2%)
-
Set blend mode to Overlay or Soft Light
This simulates natural camera grain and improves realism.
Advanced Shadow Control Techniques
Professional shadows are layered and directional.
Pro Shadow Tips:
-
Use multiple shadow layers
-
Vary opacity and blur
-
Match light direction
-
Avoid uniform shadows
This creates depth and realism instantly.
Using Adjustment Layers to Tie Everything Together
Final polish is done with global adjustments.
Useful Adjustments:
-
Curves (overall balance)
-
Color Lookup (creative grading)
-
Hue/Saturation (fine tuning)
-
Levels (contrast control)
Apply adjustments subtly and clip when necessary.
Common Advanced Mistakes to Avoid
❌ Overusing gradients
❌ Heavy reflections
❌ Extreme textures
❌ Over-stylized shadows
Advanced techniques should enhance—not distract.
Professional Workflow Tip
Advanced editors often:
-
Build the background first
-
Adjust lighting and depth
-
Then refine subject edges
-
Finalize with color grading
This top-down approach saves time and improves consistency.
Background Color Change for Different Image Types (Products, Portraits, Furniture, Fashion & Jewelry)

Not all images should be edited the same way. One of the biggest differences between beginner and professional editors is knowing which background color method works best for each image type.
In this part, you’ll learn how background color change strategies vary depending on the subject—and why using the wrong method can ruin an otherwise good image.
1. Product Photos (eCommerce & Marketplaces)
Product images demand accuracy, cleanliness, and compliance.
Primary Goals:
-
Clear product visibility
-
Accurate color representation
-
Marketplace approval (Amazon, Shopify, Etsy)
-
No halos, no distractions
Recommended Background Colors:
-
Off-white (preferred over pure white)
-
Light gray
-
Brand-neutral tones
Best Method:
-
Pen Tool + Layer Mask
-
Manual edge refinement
-
Shadow recreation under the product
Professional Notes:
-
Pure white backgrounds often look harsh
-
Soft ground shadows increase trust
-
Consistency across all product images is critical
This workflow is standard in professional product photo editing and clipping path services.
2. Portraits & Headshots (Corporate & Creative)
Portrait background color changes require subtlety. The face, hair, and skin tones must remain natural.
Primary Goals:
-
Natural skin tones
-
Soft hair edges
-
Professional mood
Recommended Background Colors:
-
Neutral gray
-
Soft beige
-
Light blue
-
Muted brand colors
Best Method:
-
Select Subject + Layer Mask
-
Manual hair refinement
-
Color temperature matching
Professional Notes:
-
Background should never overpower the face
-
Neutral tones convert better for corporate use
-
Creative portraits allow slightly stronger colors
3. Furniture & Interior Images
Furniture images are all about scale, grounding, and realism. Poor background editing makes furniture look fake instantly.
Primary Goals:
-
Preserve texture and material detail
-
Maintain realistic scale
-
Proper grounding with shadows
Recommended Background Colors:
-
Soft gray
-
Light beige
-
Interior-style neutral tones
Best Method:
-
Pen Tool for structure
-
Layer Mask refinement
-
Manual contact shadows
Professional Notes:
-
Never remove all shadows
-
Flat backgrounds without grounding reduce buyer confidence
-
Texture preservation is more important than speed
This category almost always requires manual Photoshop editing, not AI tools.
4. Fashion & Apparel Images
Fashion images involve fabric fibers, folds, and soft edges, making background color changes more complex.
Primary Goals:
-
Clean fabric edges
-
Natural folds and texture
-
No visible cutout lines
Recommended Background Colors:
-
White or off-white
-
Light gray
-
Campaign brand colors
Best Method:
-
Advanced Image Masking
-
Combination of layer masks and channels
-
Careful edge refinement
Professional Notes:
-
Avoid aggressive smoothing
-
Fabric texture must remain visible
-
Hair and clothing often require separate masking
This is why apparel editing is considered an advanced skill.
5. Jewelry & Transparent Objects (Most Difficult)
Jewelry editing is the most technically demanding category.
Why It’s Challenging:
-
Transparency
-
Reflections
-
Light refraction
-
Fine details
Recommended Background Colors:
-
Soft gray
-
Controlled gradients
-
Neutral dark or light tones
Best Method:
-
Channel-based masking
-
Multiple layer masks
-
Reflection and highlight recreation
Professional Notes:
-
AI tools almost always fail here
-
Edge contamination is common
-
Manual control is mandatory
If transparency is involved, Photoshop expertise is non-negotiable.
6. Social Media & Marketing Graphics
Marketing images allow more creative freedom—but still require discipline.
Primary Goals:
-
Visual impact
-
Brand alignment
-
Platform compatibility
Recommended Background Colors:
-
Brand colors
-
Gradients
-
High-contrast combinations
Best Method:
-
Select Subject or Pen Tool
-
Solid or gradient fill layers
-
Soft shadows or glow effects
Professional Notes:
-
Test different background colors
-
Small color changes can significantly impact engagement
-
Consistency matters across campaigns
Quick Reference Table: Best Method by Image Type
| Image Type | Best Method | Skill Level |
|---|---|---|
| Product | Pen Tool + Mask | Advanced |
| Portrait | Select Subject + Mask | Intermediate |
| Furniture | Pen Tool + Shadows | Advanced |
| Fashion | Image Masking | Advanced |
| Jewelry | Channel Masking | Expert |
| Marketing | Mixed Methods | Beginner–Intermediate |
Why Professionals Change Their Approach by Image Type
Professional editors don’t rely on one tool. They:
-
Analyze the subject
-
Choose the right method
-
Adjust color and shadows accordingly
-
Deliver purpose-driven results
This adaptability is what produces consistent, high-quality images across industries.
Professional Photoshop Workflow for Background Color Changes (How Agencies Do It at Scale)
Changing background color for one image is easy.
Changing background color for hundreds or thousands of images—consistently, accurately, and on deadline—is a completely different challenge.
This is where professional agencies and experienced editors separate themselves from casual Photoshop users.
In this part, you’ll learn how professionals handle background color changes at scale, while maintaining quality, speed, and consistency.
Why a Professional Workflow Matters
Without a structured workflow, large projects suffer from:
-
Inconsistent background colors
-
Uneven edge quality
-
Color mismatch across images
-
Slower turnaround times
-
Costly rework
A professional workflow solves these problems before they happen.
Step 1: Image Assessment Before Editing Begins
Professional teams never start editing immediately.
They first analyze:
-
Image resolution and quality
-
Edge complexity (hair, fabric, transparency)
-
Lighting direction
-
Intended platform (eCommerce, ads, print)
This assessment determines:
-
Which selection method to use
-
How much time each image needs
-
Whether automation is safe or not
Pro Insight:
Using the wrong method wastes more time than starting slow.
Step 2: Standardized Folder & File Structure
Agencies use strict file organization.
Typical Structure:
-
Originals (never edited)
-
Working PSDs
-
Final Exports
-
Client Review Files
Each PSD includes:
-
Clearly named layers
-
Grouped background, subject, and adjustments
-
Locked original layers
This prevents confusion and speeds up revisions.
Step 3: Non-Destructive Editing Only
Professional editors never destroy pixels.
Standard Rules:
-
Always use layer masks
-
Always use adjustment layers
-
Never flatten PSDs until final export
-
Keep edits reversible
This allows:
-
Easy revisions
-
Color changes without redoing work
-
Client-requested tweaks
Non-destructive editing saves time long-term.
Step 4: Batch Consistency & Color Control
For large sets, consistency matters more than individual perfection.
Professional Techniques:
-
Use reference images
-
Match background color values exactly
-
Reuse gradient presets
-
Apply identical adjustment layers
Editors often keep:
-
HEX/RGB color values documented
-
Shadow opacity standards
-
Export size presets
This ensures visual uniformity across the entire catalog.
Step 5: Quality Control (QC) Checklist
Professional agencies use a strict QC process.
QC Checklist Includes:
-
Edge quality at 300% zoom
-
No halos or color spill
-
Background color consistency
-
Natural shadows present
-
Correct export size and format
Images that fail QC are corrected before delivery—never after.
Step 6: Speed Without Sacrificing Quality
Speed comes from process, not rushing.
How Professionals Stay Fast:
-
Use the right tool for the image
-
Avoid over-editing
-
Apply reusable presets
-
Divide tasks logically in teams
AI may assist with rough selections, but final control is always manual.
Step 7: Exporting for Different Platforms
Professional exports are platform-specific.
Common Export Standards:
-
Web: JPEG / sRGB / optimized size
-
eCommerce: High-res JPEG / white or neutral background
-
Print: TIFF or high-quality JPEG
Incorrect export settings can ruin even perfect edits.
Step 8: Revision & Feedback Handling
Professionals expect revisions.
Best Practices:
-
Keep editable PSD files
-
Label version numbers clearly
-
Apply feedback consistently across all images
This builds client trust and long-term relationships.
Why Businesses Outsource Background Color Editing
Many brands outsource because:
-
In-house editing is slow
-
Consistency is hard to maintain
-
Skilled editors are expensive
-
Scale is difficult during peak seasons
Professional services deliver:
-
Faster turnaround
-
Lower cost per image
-
Consistent quality
This is why agencies and brands rely on dedicated photo editing teams.
Troubleshooting Difficult Background Color Changes (Hair, Transparency & Low-Quality Images)
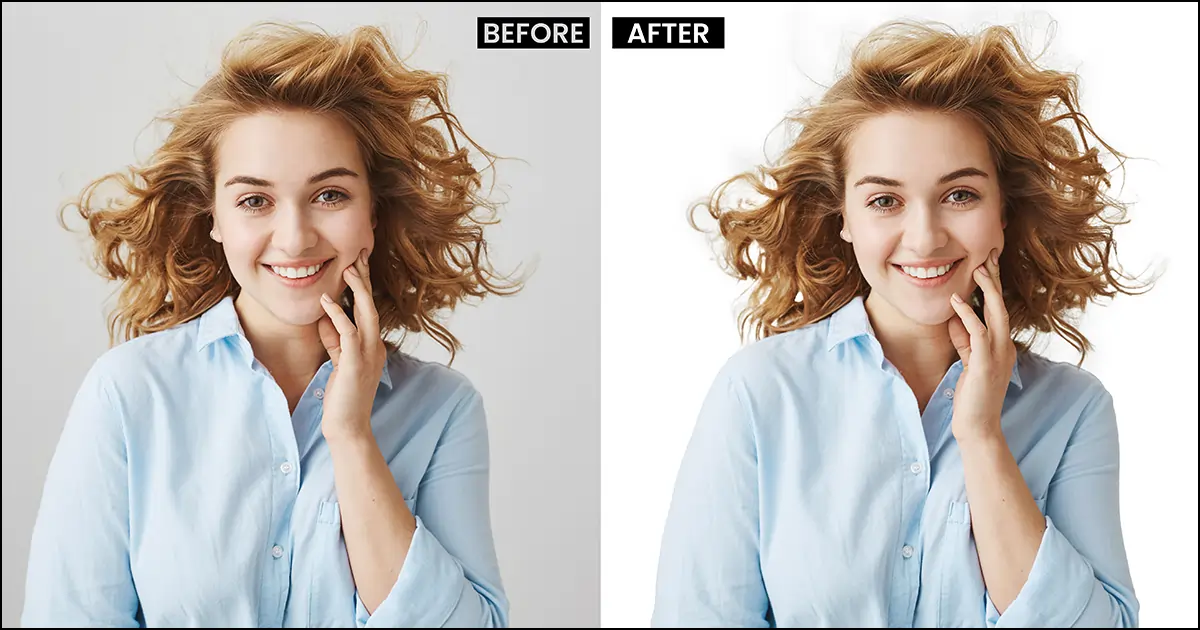

Not every image behaves nicely. In professional work, you will often face images where changing the background color feels almost impossible—hair blends into the background, transparent objects lose realism, or low-quality photos fall apart during selection.
This part explains how professionals troubleshoot the hardest background color change scenarios in Photoshop.
Problem 1: Hair Blending Into the Background
Hair is one of the most challenging elements in Photoshop because:
-
It has fine strands
-
It often blends with the background
-
Automated tools struggle with it
Why Selections Fail
-
Low contrast between hair and background
-
Overuse of Quick Selection
-
Hard-edged masking
Professional Fix:
-
Use Select and Mask
-
Paint over hair using Refine Edge Brush
-
Enable Decontaminate Colors
-
Manually refine with low-opacity brush
Pro Tip:
Don’t aim to isolate every hair strand. Aim for natural blending.
Problem 2: Fringing or Color Spill Around Edges

Fringing happens when the original background color bleeds into the subject edges.
Why It Happens:
-
Strong colored backgrounds
-
Inaccurate masking
-
Compression artifacts
How to Fix It:
-
Go to Layer > Matting > Defringe (1–2 px)
-
Use Color Balance on edges
-
Paint mask edges carefully
This is especially important when switching from dark to light backgrounds.
Problem 3: Transparent or Semi-Transparent Objects

Objects like glass, plastic, or jewelry reflect and transmit light.
Why It’s Difficult:
-
Transparency depends on background color
-
Reflections must remain realistic
-
Simple masking destroys realism
Professional Solution:
-
Use Channel-based masking
-
Keep highlights and reflections
-
Rebuild transparency manually if needed
Rule:
Never make transparent objects fully opaque.
Problem 4: Low-Resolution or Blurry Images
Low-quality images limit what Photoshop can do.
Common Issues:
-
Jagged edges
-
Noise around selections
-
Loss of detail
How Professionals Handle It:
-
Reduce contrast between subject and background
-
Use softer backgrounds
-
Avoid extreme color changes
-
Set realistic expectations
Sometimes the best solution is damage control, not perfection.
Problem 5: Complex Backgrounds with Similar Colors
When the subject color matches the background, automated tools fail.
Professional Fix:
-
Use Pen Tool where possible
-
Combine multiple selection methods
-
Manually paint the mask
-
Work slowly at high zoom
This is where experience matters more than tools.
Problem 6: Edge Looks Too Sharp or Too Soft
Why It Happens:
-
Over-feathering the mask
-
Using hard brushes
-
Incorrect feather radius
How to Fix It:
-
Use 0.5–1 px feather
-
Blend edges manually
-
Match edge softness to image resolution
Edges should match the camera’s original sharpness.
Problem 7: Background Color Change Ruins Lighting Direction

Background color alone can break realism if lighting is ignored.
Professional Fix:
-
Observe original light direction
-
Add shadows consistently
-
Avoid flat lighting
Lighting must feel logical—even subconsciously.
Professional Troubleshooting Workflow
When something looks wrong:
-
Zoom in to 300%
-
Check edges for halos
-
Match brightness first
-
Match color temperature
-
Add or refine shadows
Professionals fix issues systematically, not randomly.
When to Stop Editing
One of the most important skills is knowing when to stop.
Stop refining when:
-
Improvements become invisible
-
Edges match image quality
-
Background feels natural
Over-editing often makes images worse.
Background Color Psychology for eCommerce & Branding (High-Conversion Insight)

Changing background color in Photoshop is not just a technical task—it’s a strategic branding and conversion decision. The color behind a product or subject directly influences how customers feel, how much they trust the brand, and whether they decide to buy.
Professional eCommerce brands and advertisers choose background colors deliberately, not randomly.
Why Background Color Affects Buying Decisions
Human brains process color faster than text. Before a customer reads product details, they subconsciously react to the image.
Background color influences:
-
First impressions
-
Perceived quality
-
Trust and credibility
-
Emotional response
-
Purchase intent
This is why background color choice plays a key role in conversion optimization.
The Most Effective Background Colors for eCommerce
1. White Background (Trust & Clarity)
White is the most widely used background color in eCommerce.
Why It Works:
-
Clean and distraction-free
-
Makes products easy to evaluate
-
Accepted by all major marketplaces
-
Signals professionalism and transparency
Pro Tip:
Use off-white instead of pure white to avoid harsh contrast.
2. Light Gray (Premium & Balanced)
Light gray backgrounds feel modern and premium.
Best For:
-
Fashion and apparel
-
Electronics
-
Furniture and home decor
Gray allows product colors to stand out without overwhelming the viewer.
3. Neutral Warm Tones (Lifestyle & Comfort)
Beige, cream, and soft warm tones create a lifestyle feel.
Best For:
-
Furniture
-
Home accessories
-
Organic and handmade products
These colors evoke comfort and realism.
4. Brand Colors (Recognition & Consistency)
Using brand colors in backgrounds builds recognition.
Best Practices:
-
Keep saturation low
-
Maintain strong contrast
-
Use consistently across images
Brand colors work best for:
-
Promotional banners
-
Social media ads
-
Campaign-specific images
5. Dark Backgrounds (Luxury & Drama)
Dark backgrounds create contrast and sophistication.
Best For:
-
Jewelry
-
Luxury products
-
Watches
-
Premium electronics
⚠️ Use carefully—dark backgrounds require perfect lighting and edges.
How Background Color Impacts Perceived Product Value
Customers often associate:
-
Clean backgrounds → higher quality
-
Consistent visuals → reliable brand
-
Messy or inconsistent backgrounds → untrustworthy sellers
A poorly chosen background can reduce perceived value—even if the product itself is excellent.
Platform-Specific Background Color Strategy
Amazon
-
White or off-white preferred
-
No distractions
-
Focus entirely on the product
Shopify
-
More flexibility
-
Neutral or brand-aligned colors
-
Consistency across collections
Social Media Ads
-
High contrast works best
-
Brand colors improve recall
-
Bold but controlled backgrounds
Adapting background color to platform expectations improves performance.
Psychological Mistakes That Hurt Conversions
❌ Over-saturated backgrounds
❌ Using trendy colors without strategy
❌ Low contrast between product and background
❌ Inconsistent backgrounds across listings
Consistency builds trust. Random choices break it.
Testing Background Colors for Higher Conversions
Professional brands test background colors just like they test ad copy.
What to Test:
-
White vs light gray
-
Neutral vs brand color
-
Flat vs gradient
Small changes can lead to measurable conversion improvements.
How Professionals Use Photoshop for Color Strategy
Photoshop allows:
-
Exact color matching
-
Controlled gradients
-
Non-destructive testing
-
Easy A/B variations
This flexibility makes Photoshop ideal for conversion-focused image optimization.
When to Edit Yourself vs Outsource Background Color Editing (Time, Cost & Scale)

Learning how to change background color in Photoshop is a valuable skill—but not every situation requires you to do it yourself. As projects grow in size, complexity, or urgency, many professionals and businesses face an important decision:
Should you edit background colors yourself, or outsource the work to professionals?
The right choice depends on time, cost, scale, and quality requirements.
When It Makes Sense to Edit Background Colors Yourself
Editing in-house or by yourself is a good option when:
-
You have time to edit carefully
-
The number of images is small
-
You need full creative control
-
You’re still learning or practicing Photoshop
-
The images are not time-sensitive
Best Scenarios for DIY Editing:
-
Personal projects
-
Portfolio work
-
Small product batches
-
Creative experimentation
DIY editing builds skill—but it also consumes time.
Hidden Costs of Editing Everything Yourself
Many people underestimate the real cost of DIY editing.
Common Hidden Costs:
-
Time spent selecting, masking, refining
-
Rework due to mistakes
-
Inconsistent results across images
-
Burnout during large projects
For businesses, time spent editing is time not spent on marketing, sales, or growth.
When Outsourcing Background Color Editing Makes Sense
Outsourcing becomes the smarter option when:
-
You have large image volumes
-
Consistency across images is critical
-
Turnaround time matters
-
You need professional-grade quality
-
You want predictable results
Typical Outsourcing Use Cases:
-
eCommerce catalogs
-
Furniture and product photography
-
Fashion and apparel brands
-
Advertising agencies
-
Seasonal or bulk image updates
Professional editors follow proven workflows that reduce errors and rework.
Cost vs Value: The Real Comparison
DIY editing may look cheaper—but value matters more than cost.
| Factor | DIY Editing | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Time investment | High | Low |
| Consistency | Varies | High |
| Skill requirement | High | None |
| Scalability | Limited | Easy |
| Final quality | Depends | Professional |
For growing businesses, outsourcing often saves money in the long run.
How Professional Editing Services Work
Professional services typically offer:
-
Non-destructive Photoshop workflows
-
Quality control checks
-
Consistent background colors
-
Natural shadows and realism
-
Fast turnaround times
You get clean, ready-to-use images—without managing the editing process yourself.
Hybrid Approach Used by Smart Teams
Many professionals use a hybrid model:
-
DIY for creative or one-off edits
-
Outsource bulk or time-sensitive work
This approach balances control and efficiency.
Quality Consistency: The Biggest Advantage of Outsourcing
Consistency is hard to maintain when editing hundreds of images.
Professional teams:
-
Follow standardized color values
-
Match shadows and brightness
-
Deliver uniform results across catalogs
Consistency builds brand trust and improves customer experience.
Final Decision Guide
Choose DIY editing if:
-
You enjoy editing
-
Volume is low
-
Deadlines are flexible
Choose outsourcing if:
-
Volume is high
-
Quality affects sales
-
Speed and consistency matter
There is no wrong choice—only the right choice for your situation.
Final Takeaway of the Entire Guide
Changing background color in Photoshop is both a technical skill and a strategic decision. From selection tools and advanced masking to realism, psychology, and workflow, every step influences how an image is perceived.
Mastering this process gives you creative control. Knowing when to outsource gives you scalability and efficiency.
Together, they help you produce images that look professional, build trust, and convert better.
Case Study: How Changing Background Color Increased Conversions for an Ecommerce Brand
The Problem
An online fashion accessories brand was struggling with:
-
Inconsistent background colors across product images
-
Greyish-white tones instead of pure white
-
Distracting shadows and uneven lighting
-
High product return rate due to color perception issues
Their product page looked visually messy. Some images had cream backgrounds, others light gray, and some slightly blue-tinted whites.
The result?
-
Lower perceived brand value
-
Reduced trust
-
Decreased add-to-cart rate
The Solution
The editing team used Adobe Photoshop and implemented:
1️⃣ Object Selection Tool
To cleanly separate the product from the background.
2️⃣ Layer Mask Workflow
Instead of deleting backgrounds, they used non-destructive masking for better edge refinement.
3️⃣ Solid White Fill Layer
Set to RGB 255,255,255 for ecommerce compliance.
4️⃣ Shadow Preservation
Natural drop shadows were preserved to avoid the “floating product” effect.
The Results (After 30 Days)
After updating 120 product images:
-
📈 Conversion rate increased by 18%
-
📉 Return rate reduced by 12%
-
⏱️ Time spent on product pages increased
-
💬 Customer complaints about color mismatch dropped significantly
Why?
Because clean, consistent backgrounds:
-
Improve perceived quality
-
Make product colors appear accurate
-
Build buyer trust
-
Remove distractions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How do you change the background color in Photoshop without affecting the subject?
The best way is to:
-
Select the subject using Object Selection Tool in Adobe Photoshop
-
Click Select > Inverse to select the background
-
Add a Solid Color Fill Layer
Using a Layer Mask instead of deleting the background keeps the edit non-destructive and more professional.
2. How do I change a background to white in Photoshop?
To change the background to white:
-
Select the subject
-
Invert the selection
-
Delete the background
-
Add a Solid Color Fill Layer
-
Set RGB values to 255, 255, 255
For ecommerce platforms like Amazon, pure white (#FFFFFF) is usually required.
3. What is the fastest way to change background color in Photoshop?
The fastest method is:
-
Use Object Selection Tool
-
Click Select Subject
-
Invert selection
-
Add Solid Color Layer
This works best when the image has high contrast between subject and background.
4. How do I change the background color without deleting it?
Instead of pressing delete:
-
Add a Layer Mask
-
Mask out the background
-
Add a color layer underneath
This allows you to edit or adjust later without losing image data.
Professional retouchers prefer this workflow.
5. Why does my selection look rough or jagged?
This usually happens because:
-
Low image resolution
-
Poor contrast between subject and background
-
Incorrect feather or smooth settings
Use Select and Mask and adjust:
-
Smooth
-
Feather
-
Contrast
-
Shift Edge
Zoom in to refine small details like hair, fabric edges, or product curves.
6. How do I change the background color to any custom brand color?
After removing the background:
-
Create a Solid Color Fill Layer
-
Enter the HEX code of your brand color
-
Place the layer below your subject
This is commonly used for:
-
Ecommerce banners
-
Social ads
-
Product hero images
-
Shopify product pages
7. Can I change the background color in Photoshop without selecting the object?
Yes, if the background is a solid color, you can:
-
Use the Magic Wand Tool
-
Click on the background
-
Adjust tolerance
-
Replace it with a new fill color
However, this works best when the background is uniform and high contrast.
8. What tool is best for changing background color in Photoshop?
It depends on the image:
-
Object Selection Tool → Best for most modern edits
-
Quick Selection Tool → Good for manual control
-
Pen Tool (Clipping Path) → Best for sharp product edges
-
Layer Mask → Best for non-destructive editing
For ecommerce product images, Object Selection + Layer Mask is typically the most efficient workflow.
9. How do I keep natural shadows when changing background color?
Instead of deleting everything:
-
Refine your selection carefully
-
Preserve natural shadows
-
Add a soft brush adjustment
-
Adjust brightness/contrast slightly after adding new background
Shadows make product images look realistic and prevent the “floating object” effect.
10. Can beginners change background color in Photoshop easily?
Yes. With modern versions of Adobe Photoshop, tools like:
-
Select Subject
-
Object Selection Tool
-
Remove Background button
have made the process much easier than older versions.
Even beginners can achieve professional results with basic practice.
🚀 Ready to Standardize Your Product Backgrounds at Scale?
Changing background color in Photoshop is simple.
Maintaining visual consistency across 500+ SKUs?
That’s where most ecommerce brands struggle.
If your catalog has:
-
Inconsistent white tones
-
Uneven shadows
-
Fabric colors looking different across products
-
High return rates due to color mismatch
It’s not just an editing issue — it’s a conversion issue.
Our team specializes in background correction and ecommerce image standardization using professional workflows in Adobe Photoshop — designed specifically for scaling product catalogs.
What We Help Ecommerce Teams Achieve:
✔ Pure white (#FFFFFF) marketplace compliance
✔ Brand-consistent background tones
✔ Natural shadow preservation
✔ Bulk editing workflows
✔ Faster turnaround for large SKU volumes
📊 Let’s Audit 5 of Your Product Images (Free)
We’ll review your current background consistency and show you:
-
Where visual friction is hurting conversions
-
How background tone impacts product color accuracy
-
What workflow improvements can scale your catalog
No obligation. Just practical insight your team can use immediately.




